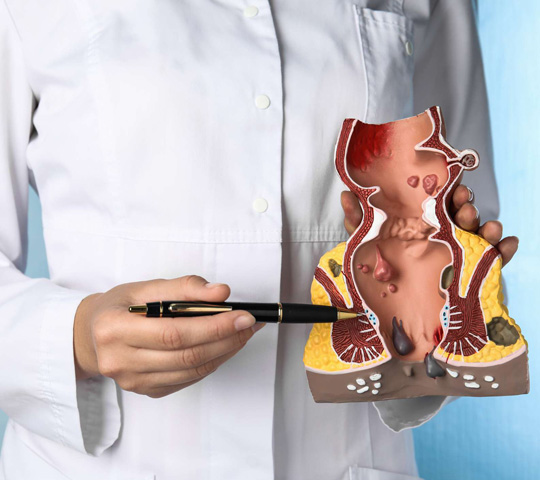
Internal piles arise from anal cushions which are 2.5cm inside the anal verge, hence not usually visible. External piles arise from below the dentate line, hence are visible in the form of swollen masses at the anal verge.
There are two types of piles: internal and external. Internal piles occur inside the rectum and are not usually visible. External piles, on the other hand, occur outside the anus and can be seen and felt.
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of piles. These include constipation, diarrhea, straining during bowel movements, and spending long periods of time sitting on the toilet. Pregnancy and obesity can also increase the risk of developing piles.
Treatment for piles depends on the severity of the condition. In many cases, simple lifestyle changes such as eating a high-fiber diet and drinking plenty of water can help alleviate symptoms. Over-the-counter creams and ointments can also be used to reduce itching and discomfort. However, these are only symptomatic treatments to cater temporary relief.
If piles are particularly severe or do not respond to self-care measures, a Proctologist may recommend more invasive treatments such as rubber band ligation or surgical removal. Definitive treatments like traditional open techniques or minimal invasive procedures.
Open techniques include rubber band ligation, Milligan Morgan removal of haemorrhoids, injection sclerotherapy. While minimal invasive techniques include Laser hemorrhoidopexy and Stapler MIPH (Minimal Invasive Procedure for Haemorrhoids)
In conclusion, piles are a common condition that affects the rectal and anal area, caused by the swelling of the veins. It can be treated with self-care measures or with the help of a Proctologist